Contents
Articles
2025
- The Android Management API doesn't support pulling managed properties (config) from app tracks. Here's how to work around it
- Hands-on with CVE-2025-22442, a work profile sideloading vulnerability affecting most Android devices today
- AAB support for private apps in the managed Google Play iFrame is coming, take a first look here
- What's new (so far) for enterprise in Android 16
2024
- Android 15: What's new for enterprise?
- How Goto's acquisition of Miradore is eroding a once-promising MDM solution
- Google Play Protect no longer sends sideloaded applications for scanning on enterprise-managed devices
- Mobile Pros is moving to Discord
- Avoid another CrowdStrike takedown: Two approaches to replacing Windows
- Introducing MANAGED SETTINGS
- I'm joining NinjaOne
- Samsung announces Knox SDK restrictions for Android 15
- What's new (so far) for enterprise in Android 15
- Google quietly introduces new quotas for unvalidated AMAPI use
- What is Play Auto Install (PAI) in Android and how does it work?
- AMAPI publicly adds support for DPC migration
- How do Android devices become certified?
2023
- Mute @channel & @here notifications in Slack
- A guide to raising better support requests
- Ask Jason: How should we manage security and/or OS updates for our devices?
- Pixel 8 series launches with 7 years of software support
- Android's work profile behaviour has been reverted in 14 beta 5.3
- Fairphone raises the bar with commitment to Android updates
- Product files: The DoorDash T8
- Android's work profile gets a major upgrade in 14
- Google's inactive account policy may not impact Android Enterprise customers
- Product files: Alternative form factors and power solutions
- What's new in Android 14 for enterprise
- Introducing Micro Mobility
- Android Enterprise: A refresher
2022
- What I'd like to see from Android Enterprise in 2023
- Thoughts on Android 12's password complexity changes
- Google Play target API requirements & impact on enterprise applications
- Sunsetting Discuss comment platform
- Google publishes differences between Android and Android Go
- Android Go & EMM support
- Relaunching bayton.org
- AER dropped the 3/5 year update mandate with Android 11, where are we now?
- I made a bet with Google (and lost)
2020
- Product files: Building Android devices
- Google announce big changes to zero-touch
- VMware announces end of support for Device Admin
- Google launch the Android Enterprise Help Community
- Watch: An Android Enterprise discussion with Hypergate
- Listen again: BM podcast #144 - Jason Bayton & Russ Mohr talk Android!
- Google's Android Management API will soon support COPE
- Android Enterprise in 11: Google reduces visibility and control with COPE to bolster privacy.
- The decade that redefined Android in the enterprise
2019
- Why Intune doesn't support Android Enterprise COPE
- VMware WS1 UEM 1908 supports Android Enterprise enrolments on closed networks and AOSP devices
- The Bayton 2019 Android Enterprise experience survey
- Android Enterprise Partner Summit 2019 highlights
- The Huawei ban and Enterprise: what now?
- Dabbling with Android Enterprise in Q beta 3
- Why I moved from Google WiFi to Netgear Orbi
- I'm joining Social Mobile as Director of Android Innovation
- Android Enterprise in Q/10: features and clarity on DA deprecation
- MWC 2019: Mid-range devices excel, 5G everything, form-factors galore and Android Enterprise
- UEM tools managing Android-powered cars
- Joining the Android Enterprise Experts community
- February was an interesting month for OEMConfig
- Google launch Android Enterprise Recommended for Managed Service Providers
- Migrating from Windows 10 Mobile? Here's why you should consider Android
- AER expands: Android Enterprise Recommended for EMMs
- What I'd like to see from Android Enterprise in 2019
2018
- My top Android apps in 2018
- Year in review: 2018
- MobileIron Cloud R58 supports Android Enterprise fully managed devices with work profiles
- Hands on with the Huawei Mate 20 Pro
- Workspace ONE UEM 1810 introduces support for Android Enterprise fully managed devices with work profiles
- G Suite no longer prevents Android data leakage by default
- Live: Huawei Mate series launch
- How to sideload the Digital Wellbeing beta on Pie
- How to manually update the Nokia 7 Plus to Android Pie
- Hands on with the BQ Aquaris X2 Pro
- Hands on with Sony OEMConfig
- The state of Android Enterprise in 2018
- BYOD & Privacy: Don’t settle for legacy Android management in 2018
- Connecting two Synologies via SSH using public and private key authentication
- How to update Rsync on Mac OS Mojave and High Sierra
- Intune gains support for Android Enterprise COSU deployments
- Android Enterprise Recommended: HMD Global launch the Nokia 3.1 and Nokia 5.1
- Android Enterprise Partner Summit 2018 highlights
- Live: MobileIron LIVE! 2018
- Android Enterprise first: AirWatch 9.4 lands with a new name and focus
- Live: Android Enterprise Partner Summit 2018
- Samsung, Oreo and an inconsistent Android Enterprise UX
- MobileIron launch Android Enterprise work profiles on fully managed devices
- Android P demonstrates Google's focus on the enterprise
- An introduction to managed Google Play
- MWC 2018: Android One, Oreo Go, Android Enterprise Recommended & Android Enterprise
- Enterprise ready: Google launch Android Enterprise Recommended
2017
- Year in review: 2017
- Google is deprecating device admin in favour of Android Enterprise
- Hands on with the Sony Xperia XZ1 Compact
- Moto C Plus giveaway
- The state of Android Enterprise in 2017
- Samsung launched a Note 8 for enterprise
- MobileIron officially supports Android Enterprise QR code provisioning
- Android zero-touch enrolment has landed
- MobileIron unofficially supports QR provisioning for Android Enterprise work-managed devices, this is how I found it
- Hands on with the Nokia 3
- Experimenting with clustering and data replication in Nextcloud with MariaDB Galera and SyncThing
- Introducing documentation on bayton.org
- Goodbye Alexa, Hey Google: Hands on with the Google Home
- Restricting access to Exchange ActiveSync
- What is Mobile Device Management?
- 8 tips for a successful EMM deployment
- Long-term update: the fitlet-RM, a fanless industrial mini PC by Compulab
- First look: the FreedomPop V7
- Vault7 and the CIA: This is why we need EMM
- What is Android Enterprise (Android for Work) and why is it used?
- Introducing night mode on bayton.org
- What is iOS Supervision and why is it used?
- Hands on with the Galaxy TabPro S
- Introducing Nextcloud demo servers
- Part 4 - Project Obsidian: Obsidian is dead, long live Obsidian
2016
- My top Android apps 2016
- Hands on with the Linx 12V64
- Wandera review 2016: 2 years on
- Deploying MobileIron 9.1+ on KVM
- Hands on with the Nextcloud Box
- How a promoted tweet landed me on Finnish national news
- Using RWG Mobile for simple, cross-device centralised voicemail
- Part 3 – Project Obsidian: A change, data migration day 1 and build day 2
- Hands on: fitlet-RM, a fanless industrial mini PC by Compulab
- Part 2 - Project Obsidian: Build day 1
- Part 1 - Project Obsidian: Objectives & parts list
- Part 0 - Project Obsidian: Low power NAS & container server
- 5 Android apps improving my Chromebook experience
- First look: Android apps on ChromeOS
- Competition: Win 3 months of free VPS/Container hosting - Closed!
- ElasticHosts review
- ElasticHosts: Cloud Storage vs Folders, what's the difference?
- Adding bash completion to LXD
- Android N: First look & hands-on
- Springs.io - Container hosting at container prices
- Apple vs the FBI: This is why we need MDM
- Miradore Online MDM: Expanding management with subscriptions
- Lenovo Yoga 300 (11IBY) hard drive upgrade
- I bought a Lenovo Yoga 300, this is why I'm sending it back
- Restricting access to Exchange ActiveSync
- Switching to HTTPS on WordPress
2015
2014
- Is CYOD the answer to the BYOD headache?
- BYOD Management: Yes, we can wipe your phone
- A fortnight with Android Wear: LG G Watch review
- First look: Miradore Online free MDM
- Hands on: A weekend with Google Glass
- A month with Wandera Mobile Gateway
- Final thoughts: Dell Venue Pro 11 (Atom)
- Thoughts on BYOD
- Will 2014 bring better battery life?
- My year in review: Bayton.org
- The best purchase I've ever made? A Moto G for my father
2013
2012
- My Top Android Apps 12/12
- The Nexus 7 saga: Resolved
- Recycling Caps Lock into something useful - Ubuntu (12.04)
- The Nexus 7 saga continues
- From Wows to Woes: Why I won't be recommending a Nexus7 any time soon.
- Nexus7: What you need to know
- Why I disabled dlvr.it links on Facebook
- HTC Sense: Changing the lockscreen icons from within ADW
2011
- Push your Google+ posts to Twitter and Facebook
- Using multiple accounts with Google.
- The "Wn-R48" (Windows on the Cr-48)
- Want a Google+ invite?
- Publishing to external sources from Google+
- Dell Streak review. The Phone/Tablet Hybrid
- BlueInput: The Bluetooth HID driver Google forgot to include
- Pushing Buzz to Twitter with dlvr.it
- Managing your social outreach with dlvr.it
- When Awe met Some. The Cr-48 and Gnome3.
- Living with Google's Cr-48 and the cloud.
- Downtime 23-25/04/2011
- Are you practising "safe surfing"?
- The Virtualbox bug: "Cannot access the kernel driver" in Windows
- Putting tech into perspective
2010
- Have a Google Buzz Christmas
- Root a G1 running Android 1.6 without recovery!
- Windows 7 display issues on old Dell desktops
- Google added the Apps flexibility we've been waiting for!
- Part I: My 3 step program for moving to Google Apps
- Downloading torrents
- Completing the Buzz experience for Google Maps Mobile
- Quicktip: Trial Google Apps
- Quicktip: Save internet images fast
- Turn your desktop 3D!
- Part III - Device not compatible - Skype on 3
- Swype not compatible? ShapeWriter!
- Don't wait, get Swype now!
- HideIP VPN. Finally!
- Google enables Wave for Apps domains
- Aspire One touch screen
- Streamline XP into Ubuntu
- Edit a PDF with Zamzar
- Google offering Gmail addresses in the UK
- Google Wave: Revolutionising blogs!
- Hexxeh's Google Chrome OS builds
- Update: Buzz on Windows Mobile
- Alternatives to Internet Explorer
- Wordress 3.0 is coming!
- Skype for WM alternatives
- Browsing on a (data) budget? Opera!
- Buzz on unsupported mobiles
- Buzz on your desktop
- What's all the Buzz?
- Part II: Device not compatible - Skype on 3
- Part I - Device not compatible - Skype on 3
- Dreamscene on Windows 7
- Free Skype with 3? There's a catch..
Restricting access to Exchange ActiveSync
Contents
Introduction
#By default, Exchange allows connections to ActiveSync from anywhere in the world. While this is great for new Exchange admins, small businesses who don’t want to do much configuration and those who want things to just work, it poses a security risk on par with any other service openly accessible over the internet.
As Enterprise Mobility continues to grow and management platforms become more prevalent within the industry, leaving ActiveSync completely open is making less and less sense both from a security and management perspective.
Once devices are fully managed and ActiveSync profiles have been configured and deployed, limiting access to ActiveSync externally will prevent devices circumventing MDM in order to access email on their mobile devices. With circumvention impossible, end-users are required to enroll their devices onto the corporate MDM platform in order to get their email, enabling greater control over the devices in general; a benefit in its own right.
The aim of this guide is to provide directions for restricting access to ActiveSync to only specified, whitelisted IP addresses; these may be for a MobileIron Sentry, an AirWatch SEG or any other ActiveSync proxy that may be in use in the business. When finished, it will only be possible to connect to ActiveSync through the specified, whitelisted service, whether on-site or remote.
Before you begin
#- This guide uses Microsoft IIS configurations to restrict access. For firewall configuration this guide is not suitable.
- The directions outlined below will only restrict access to ActiveSync, leaving OWA (Outlook Web Access) traffic untouched.
- Although aimed at the EMM industry, this guide is suitable for any ActiveSync proxy, or just to keep ActiveSync locked down.
- Despite being shown on a Windows 2012 R2 server, the same steps apply on earlier versions of Windows Server.
If you are happy to proceed, please read on.
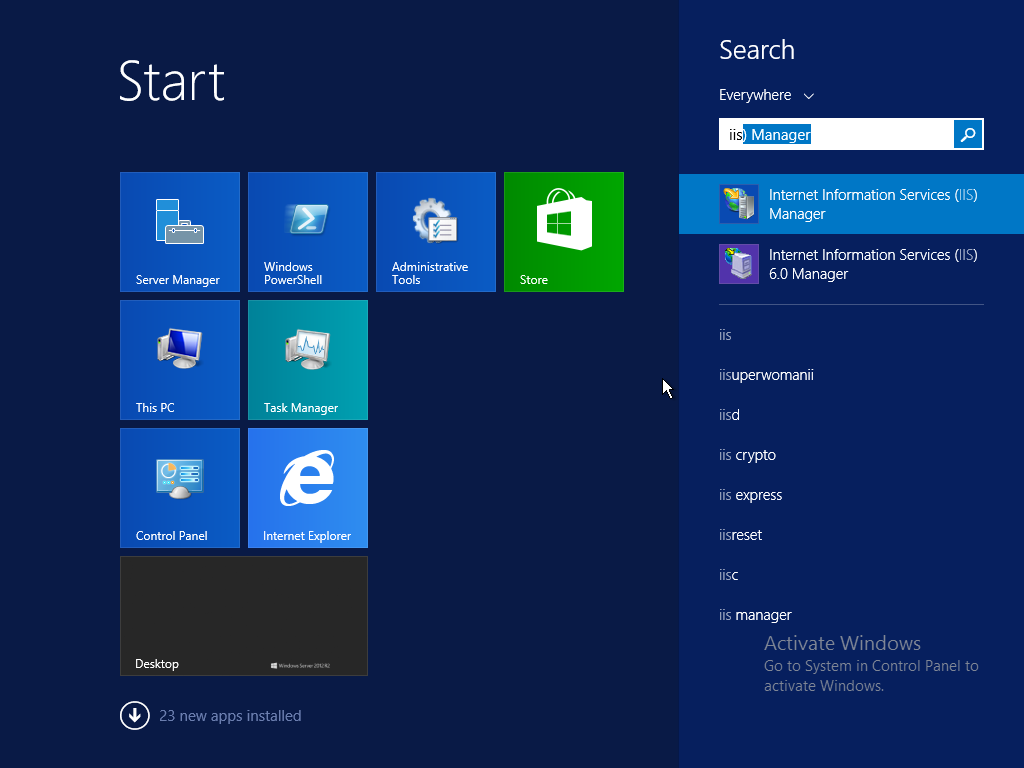
Open IIS Manager
#Click start and open IIS Manager from the start menu. On Server 2012 just type IIS within the Start Window and it will appear, for older Windows Server versions it’ll be under All Programs > Administrative tools.
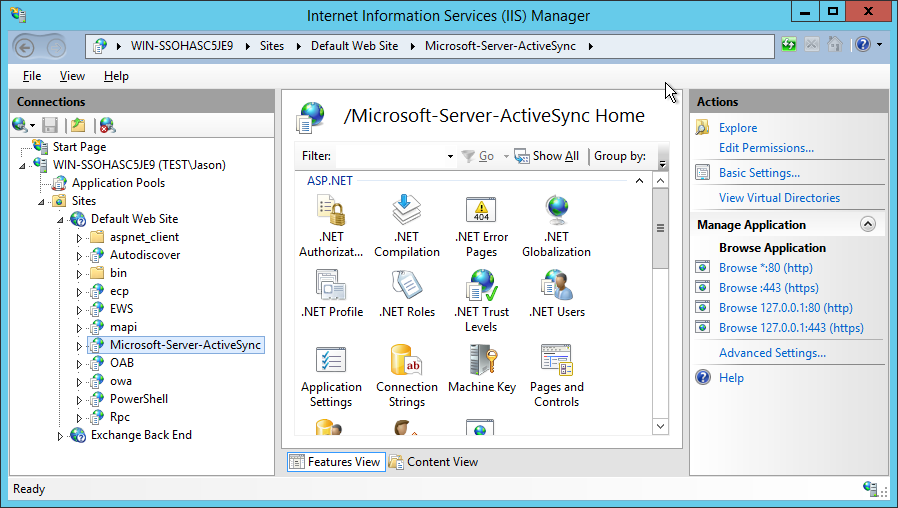
Locate Microsoft-Server-ActiveSync
#In the new window, expand the Servername, followed by Sites, Default Web Site and scroll until you find Microsoft-Server-Activesync.
Select this.
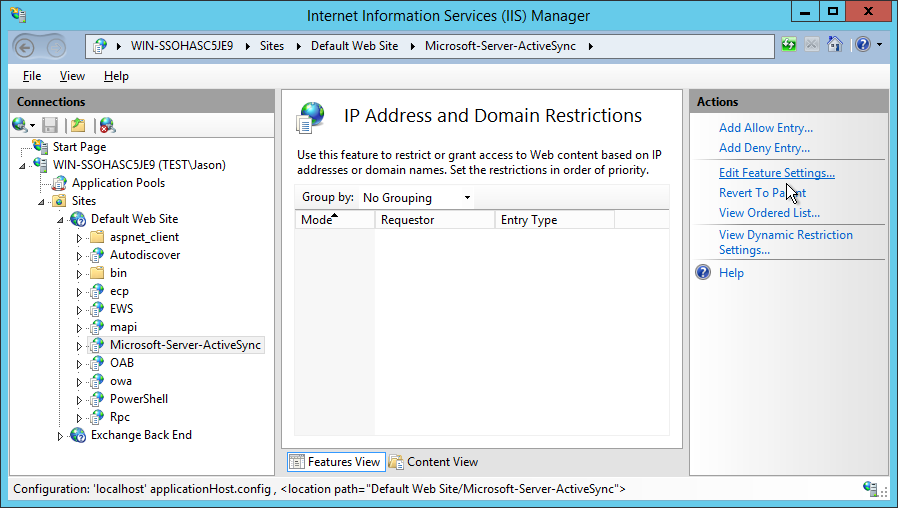
Open IP Address & Domain Restrictions
#Once selected, in the main console will be a number of settings to choose from. Find and select IP Address and Domain Restrictions. Double click to open.
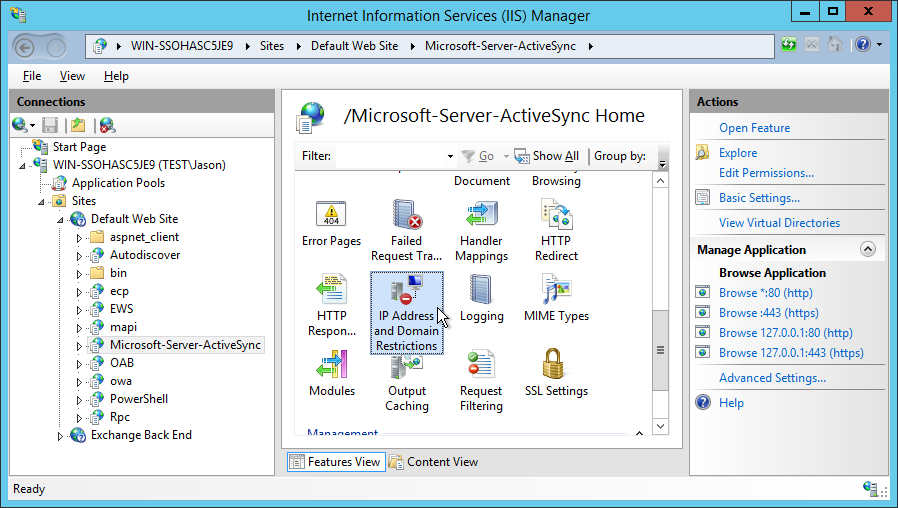
Is IP Address and Domain Restrictions missing? It may need to to be added using Add features in Server Manager.
Add Allow Entry
#Once open, the Actions pane on the right-hand toolbar will show Add Allow Entry. For this guide we will add the allow entry before denying access.
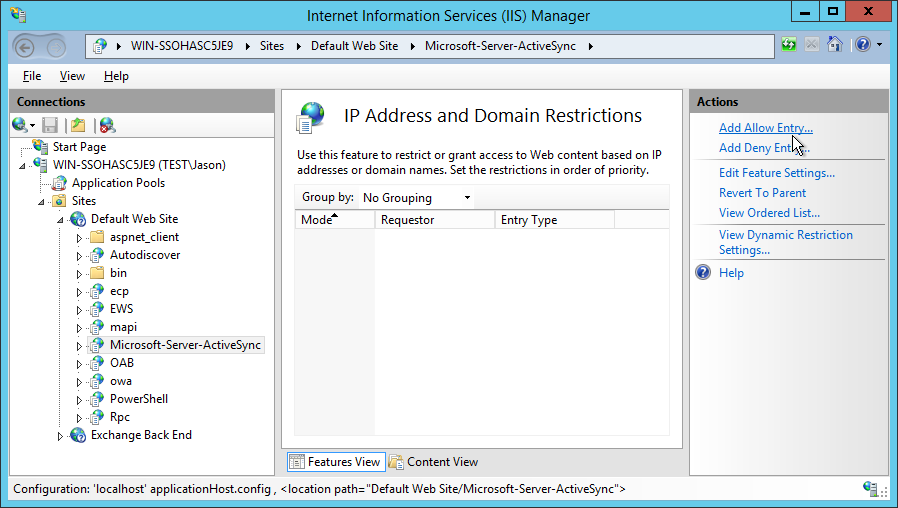
Click Add Allow Entry and a new window in which to put the IP address of the whitelisted service will pop up. Enter the address(es) here and click OK to close.
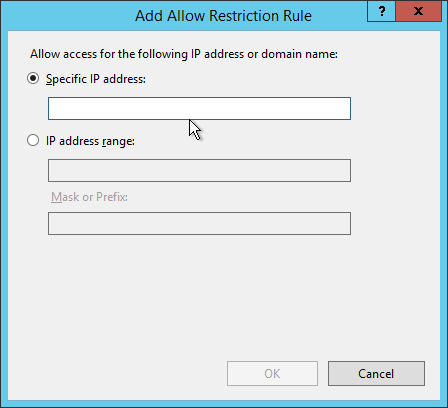
For those with an on premise application, input the internal IP.
For those with a hosted/cloud service, ping the public URL to obtain the public IP address.
Edit Feature Settings
#With the whitelisted application in place, we’ll now prevent all other traffic from connecting to ActiveSync.
As mentioned above, Exchange permits traffic from anywhere. This means anyone with an ActiveSync device can try to connect to the server irrespective of whether or not they are permitted to do so. In this step that option will be revoked, meaning only devices connecting through the whitelisted application can make an ActiveSync connection (and only MDM-enrolled devices are able to utilise this service, increasing security dramatically).
Going back to the Actions pane on the right-hand side, select Edit Feature Settings.
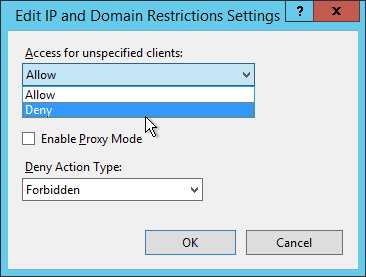
Deny unspecified clients
#This will bring up a new window. In here, select the dropdown for Access for unspecified clients and change it to Deny. Click OK to close.
Restart IIS
#Finally in order for the changes to take effect, IIS will need to be restarted. The exchange server can remain online for this if we opt for an iisreset, otherwise schedule downtime accordingly and test access to ActiveSync both through the whitelisted service and externally to confirm changes have been successfully applied.
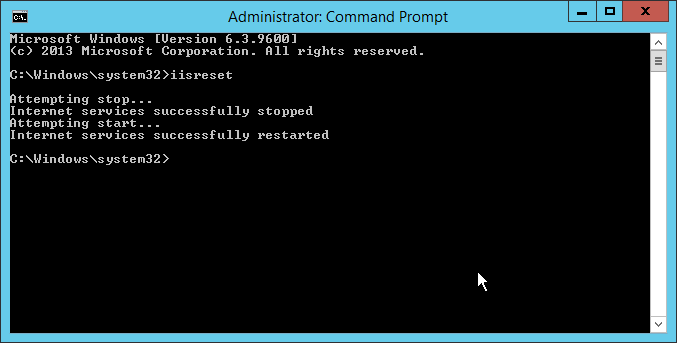
IIS will be unavailable for a number of seconds while an iisreset is being performed. The business may need to be aware of any disruptions so plan accordingly.
Articles
2025
- The Android Management API doesn't support pulling managed properties (config) from app tracks. Here's how to work around it
- Hands-on with CVE-2025-22442, a work profile sideloading vulnerability affecting most Android devices today
- AAB support for private apps in the managed Google Play iFrame is coming, take a first look here
- What's new (so far) for enterprise in Android 16
2024
- Android 15: What's new for enterprise?
- How Goto's acquisition of Miradore is eroding a once-promising MDM solution
- Google Play Protect no longer sends sideloaded applications for scanning on enterprise-managed devices
- Mobile Pros is moving to Discord
- Avoid another CrowdStrike takedown: Two approaches to replacing Windows
- Introducing MANAGED SETTINGS
- I'm joining NinjaOne
- Samsung announces Knox SDK restrictions for Android 15
- What's new (so far) for enterprise in Android 15
- Google quietly introduces new quotas for unvalidated AMAPI use
- What is Play Auto Install (PAI) in Android and how does it work?
- AMAPI publicly adds support for DPC migration
- How do Android devices become certified?
2023
- Mute @channel & @here notifications in Slack
- A guide to raising better support requests
- Ask Jason: How should we manage security and/or OS updates for our devices?
- Pixel 8 series launches with 7 years of software support
- Android's work profile behaviour has been reverted in 14 beta 5.3
- Fairphone raises the bar with commitment to Android updates
- Product files: The DoorDash T8
- Android's work profile gets a major upgrade in 14
- Google's inactive account policy may not impact Android Enterprise customers
- Product files: Alternative form factors and power solutions
- What's new in Android 14 for enterprise
- Introducing Micro Mobility
- Android Enterprise: A refresher
2022
- What I'd like to see from Android Enterprise in 2023
- Thoughts on Android 12's password complexity changes
- Google Play target API requirements & impact on enterprise applications
- Sunsetting Discuss comment platform
- Google publishes differences between Android and Android Go
- Android Go & EMM support
- Relaunching bayton.org
- AER dropped the 3/5 year update mandate with Android 11, where are we now?
- I made a bet with Google (and lost)
2020
- Product files: Building Android devices
- Google announce big changes to zero-touch
- VMware announces end of support for Device Admin
- Google launch the Android Enterprise Help Community
- Watch: An Android Enterprise discussion with Hypergate
- Listen again: BM podcast #144 - Jason Bayton & Russ Mohr talk Android!
- Google's Android Management API will soon support COPE
- Android Enterprise in 11: Google reduces visibility and control with COPE to bolster privacy.
- The decade that redefined Android in the enterprise
2019
- Why Intune doesn't support Android Enterprise COPE
- VMware WS1 UEM 1908 supports Android Enterprise enrolments on closed networks and AOSP devices
- The Bayton 2019 Android Enterprise experience survey
- Android Enterprise Partner Summit 2019 highlights
- The Huawei ban and Enterprise: what now?
- Dabbling with Android Enterprise in Q beta 3
- Why I moved from Google WiFi to Netgear Orbi
- I'm joining Social Mobile as Director of Android Innovation
- Android Enterprise in Q/10: features and clarity on DA deprecation
- MWC 2019: Mid-range devices excel, 5G everything, form-factors galore and Android Enterprise
- UEM tools managing Android-powered cars
- Joining the Android Enterprise Experts community
- February was an interesting month for OEMConfig
- Google launch Android Enterprise Recommended for Managed Service Providers
- Migrating from Windows 10 Mobile? Here's why you should consider Android
- AER expands: Android Enterprise Recommended for EMMs
- What I'd like to see from Android Enterprise in 2019
2018
- My top Android apps in 2018
- Year in review: 2018
- MobileIron Cloud R58 supports Android Enterprise fully managed devices with work profiles
- Hands on with the Huawei Mate 20 Pro
- Workspace ONE UEM 1810 introduces support for Android Enterprise fully managed devices with work profiles
- G Suite no longer prevents Android data leakage by default
- Live: Huawei Mate series launch
- How to sideload the Digital Wellbeing beta on Pie
- How to manually update the Nokia 7 Plus to Android Pie
- Hands on with the BQ Aquaris X2 Pro
- Hands on with Sony OEMConfig
- The state of Android Enterprise in 2018
- BYOD & Privacy: Don’t settle for legacy Android management in 2018
- Connecting two Synologies via SSH using public and private key authentication
- How to update Rsync on Mac OS Mojave and High Sierra
- Intune gains support for Android Enterprise COSU deployments
- Android Enterprise Recommended: HMD Global launch the Nokia 3.1 and Nokia 5.1
- Android Enterprise Partner Summit 2018 highlights
- Live: MobileIron LIVE! 2018
- Android Enterprise first: AirWatch 9.4 lands with a new name and focus
- Live: Android Enterprise Partner Summit 2018
- Samsung, Oreo and an inconsistent Android Enterprise UX
- MobileIron launch Android Enterprise work profiles on fully managed devices
- Android P demonstrates Google's focus on the enterprise
- An introduction to managed Google Play
- MWC 2018: Android One, Oreo Go, Android Enterprise Recommended & Android Enterprise
- Enterprise ready: Google launch Android Enterprise Recommended
2017
- Year in review: 2017
- Google is deprecating device admin in favour of Android Enterprise
- Hands on with the Sony Xperia XZ1 Compact
- Moto C Plus giveaway
- The state of Android Enterprise in 2017
- Samsung launched a Note 8 for enterprise
- MobileIron officially supports Android Enterprise QR code provisioning
- Android zero-touch enrolment has landed
- MobileIron unofficially supports QR provisioning for Android Enterprise work-managed devices, this is how I found it
- Hands on with the Nokia 3
- Experimenting with clustering and data replication in Nextcloud with MariaDB Galera and SyncThing
- Introducing documentation on bayton.org
- Goodbye Alexa, Hey Google: Hands on with the Google Home
- Restricting access to Exchange ActiveSync
- What is Mobile Device Management?
- 8 tips for a successful EMM deployment
- Long-term update: the fitlet-RM, a fanless industrial mini PC by Compulab
- First look: the FreedomPop V7
- Vault7 and the CIA: This is why we need EMM
- What is Android Enterprise (Android for Work) and why is it used?
- Introducing night mode on bayton.org
- What is iOS Supervision and why is it used?
- Hands on with the Galaxy TabPro S
- Introducing Nextcloud demo servers
- Part 4 - Project Obsidian: Obsidian is dead, long live Obsidian
2016
- My top Android apps 2016
- Hands on with the Linx 12V64
- Wandera review 2016: 2 years on
- Deploying MobileIron 9.1+ on KVM
- Hands on with the Nextcloud Box
- How a promoted tweet landed me on Finnish national news
- Using RWG Mobile for simple, cross-device centralised voicemail
- Part 3 – Project Obsidian: A change, data migration day 1 and build day 2
- Hands on: fitlet-RM, a fanless industrial mini PC by Compulab
- Part 2 - Project Obsidian: Build day 1
- Part 1 - Project Obsidian: Objectives & parts list
- Part 0 - Project Obsidian: Low power NAS & container server
- 5 Android apps improving my Chromebook experience
- First look: Android apps on ChromeOS
- Competition: Win 3 months of free VPS/Container hosting - Closed!
- ElasticHosts review
- ElasticHosts: Cloud Storage vs Folders, what's the difference?
- Adding bash completion to LXD
- Android N: First look & hands-on
- Springs.io - Container hosting at container prices
- Apple vs the FBI: This is why we need MDM
- Miradore Online MDM: Expanding management with subscriptions
- Lenovo Yoga 300 (11IBY) hard drive upgrade
- I bought a Lenovo Yoga 300, this is why I'm sending it back
- Restricting access to Exchange ActiveSync
- Switching to HTTPS on WordPress
2015
2014
- Is CYOD the answer to the BYOD headache?
- BYOD Management: Yes, we can wipe your phone
- A fortnight with Android Wear: LG G Watch review
- First look: Miradore Online free MDM
- Hands on: A weekend with Google Glass
- A month with Wandera Mobile Gateway
- Final thoughts: Dell Venue Pro 11 (Atom)
- Thoughts on BYOD
- Will 2014 bring better battery life?
- My year in review: Bayton.org
- The best purchase I've ever made? A Moto G for my father
2013
2012
- My Top Android Apps 12/12
- The Nexus 7 saga: Resolved
- Recycling Caps Lock into something useful - Ubuntu (12.04)
- The Nexus 7 saga continues
- From Wows to Woes: Why I won't be recommending a Nexus7 any time soon.
- Nexus7: What you need to know
- Why I disabled dlvr.it links on Facebook
- HTC Sense: Changing the lockscreen icons from within ADW
2011
- Push your Google+ posts to Twitter and Facebook
- Using multiple accounts with Google.
- The "Wn-R48" (Windows on the Cr-48)
- Want a Google+ invite?
- Publishing to external sources from Google+
- Dell Streak review. The Phone/Tablet Hybrid
- BlueInput: The Bluetooth HID driver Google forgot to include
- Pushing Buzz to Twitter with dlvr.it
- Managing your social outreach with dlvr.it
- When Awe met Some. The Cr-48 and Gnome3.
- Living with Google's Cr-48 and the cloud.
- Downtime 23-25/04/2011
- Are you practising "safe surfing"?
- The Virtualbox bug: "Cannot access the kernel driver" in Windows
- Putting tech into perspective
2010
- Have a Google Buzz Christmas
- Root a G1 running Android 1.6 without recovery!
- Windows 7 display issues on old Dell desktops
- Google added the Apps flexibility we've been waiting for!
- Part I: My 3 step program for moving to Google Apps
- Downloading torrents
- Completing the Buzz experience for Google Maps Mobile
- Quicktip: Trial Google Apps
- Quicktip: Save internet images fast
- Turn your desktop 3D!
- Part III - Device not compatible - Skype on 3
- Swype not compatible? ShapeWriter!
- Don't wait, get Swype now!
- HideIP VPN. Finally!
- Google enables Wave for Apps domains
- Aspire One touch screen
- Streamline XP into Ubuntu
- Edit a PDF with Zamzar
- Google offering Gmail addresses in the UK
- Google Wave: Revolutionising blogs!
- Hexxeh's Google Chrome OS builds
- Update: Buzz on Windows Mobile
- Alternatives to Internet Explorer
- Wordress 3.0 is coming!
- Skype for WM alternatives
- Browsing on a (data) budget? Opera!
- Buzz on unsupported mobiles
- Buzz on your desktop
- What's all the Buzz?
- Part II: Device not compatible - Skype on 3
- Part I - Device not compatible - Skype on 3
- Dreamscene on Windows 7
- Free Skype with 3? There's a catch..